7.8 Git Tools - Advanced Merging
终止合并
可以用 git merge --abort,就不要用 git reset --hard 了。
合并的时候忽略空白字符
git merge 时加入参数 -Xignore-all-space or -Xignore-space-change。
最好还是不用,因为这样容易出现混合的换行方式(\n 和 \r\n)。
手动 re-merging
讲的是 git merge-file 的用法。和手动修改相比,这样做更容易脚本化,因为很多命令行工具只能对没有 conflict markers 的源码处理。
首先,冲突已经发生。我们获取冲突文件的三个版本:
$ git show :1:hello.rb > hello.common.rb
$ git show :2:hello.rb > hello.ours.rb
$ git show :3:hello.rb > hello.theirs.rb
The
:1:hello.rbis just a shorthand for looking up that blob SHA-1.
获得这样三份文件之后,我们可以修改 hello.theirs.rb 的内容,然后做一次合并(注意文件的出现顺序是 <current-file> <base-file> <other-file>):
$ git merge-file -p hello.ours.rb hello.common.rb hello.theirs.rb > hello.rb
-p 选项是将结果写入标准输出流,而不是直接改当前文件(当前文件是 hello.ours.rb,但是这显然不是我们最终要修改的文件)。
这个做法比直接使用忽略空白字符更好,因为我们转换了整个文件,不会出现混合的换行风格。
In fact, this actually works better than the
ignore-space-changeoption because this actually fixes the whitespace changes before merge instead of simply ignoring them. In theignore-space-changemerge, we actually ended up with a few lines with DOS line endings, making things mixed.
如果仓库里面没有其他重要文件的话,现在可以用 git clean -f 来删除刚刚为了合并而创建的冗余文件。
Checking-out conflicts
假定已经合并失败,现在失败的那些文件会包含有两个分支的代码块。可以手动 checkout 一次获得含三个分支的代码块(多出来的一个是两个冲突分支之前的 base 分支所包含的代码)。
You can pass
--conflicteitherdiff3ormerge(which is the default). If you pass itdiff3, Git will use a slightly different version of conflict markers, not only giving you the “ours” and “theirs” versions, but also the “base” version inline to give you more context.
$ git checkout --conflict=diff3 hello.rb
Once we run that, the file will look like this instead:
#! /usr/bin/env ruby
def hello
<<<<<<< ours
puts 'hola world'
||||||| base
puts 'hello world'
=======
puts 'hello mundo'
>>>>>>> theirs
end
hello()
Combined-diff
在冲突之后运行 git diff:
$ git diff
diff --cc hello.rb
index 0399cd5,59727f0..0000000
--- a/hello.rb
+++ b/hello.rb
@@@ -1,7 -1,7 +1,11 @@@
#! /usr/bin/env ruby
def hello
++<<<<<<< HEAD
+ puts 'hola world'
++=======
+ puts 'hello mundo'
++>>>>>>> mundo
end
hello()
The format is called “Combined Diff” and gives you two columns of data next to each line.
一般的 diff 只有一行标志。
可以看出来冲突 marker 本身也被标记上了,而且是在 ours 和 theirs 上都有加号,因为它本来就是工作区相对于两个分支新增的。
MERGE_HEAD
在 A 分支,运行 git merge B,但是因为 merge 冲突留在了中间状态。这个时候 HEAD 是 A,而 MERGE_HEAD 是 B。
revert
假设 M 是一个错误合并。master 想要不合并这个分支除了使用 git reset --hard 改写历史之外,还可以用 git revert -m 1 HEAD,其中 -m 1 是指定 parent。对于 merge commit 而言,revert 它就相当于使得这个 merge 变成了 fake merge。
但是,如果之后还想要合并 topic 分支就会出现问题。因为我们之前用了 revert,topic 这一段 commits 被认为是我们不需要的。如图,创建合并 C8,只有 C7 这一个 commit 会被带入 C8,而 C3 和 C4 会被忽略。
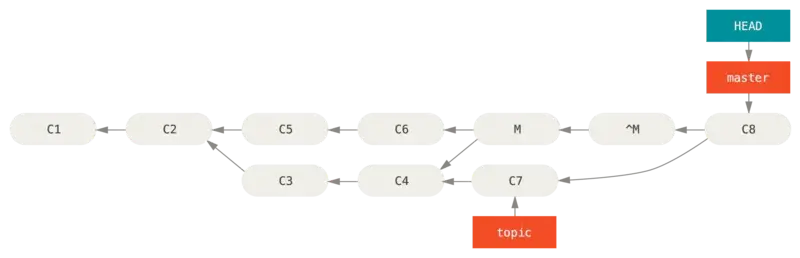
为了解决这个问题,我们需要用 git revert ^M 来再次 revert 之前的 commit(这里由于只有一个 parent 所以不需要指定 revert 路径),然后合并 topic。这样 C3、C4、C7 的改动都会包含在最终的 commit 里。
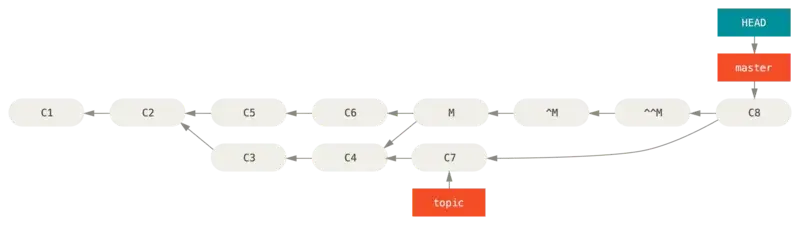
这篇文章的例子很好: https://itnext.io/git-revert-the-revert-88b1e66d71d4
从设计逻辑上来思考这个问题:revert 的作用是隐瞒一段 commits。revert 一个 revert(也就是 unrevert)会使得之前隐瞒的 commits 重新被看到。按照这样的逻辑,在 ^^M 这一步时 C3 和 C4 的修改就已经出现了。而 C8 只是合并了 C7。
尝试从文件版本上解释这个问题:^M 是将 M revert,因而文件版本是 C6。而 ^^M 是对 ^M revert,所以文件版本是 ^M 之前的 M,而 M 中已经包含了 C3 和 C4 的改动。如果在 revert ^M 的时候,要复原的相关文件已经被改动过了,那么就可能在改动区域出现冲突,需要像 merge、rebase 那样解决冲突才能正常 revert。
一般的工作流程:
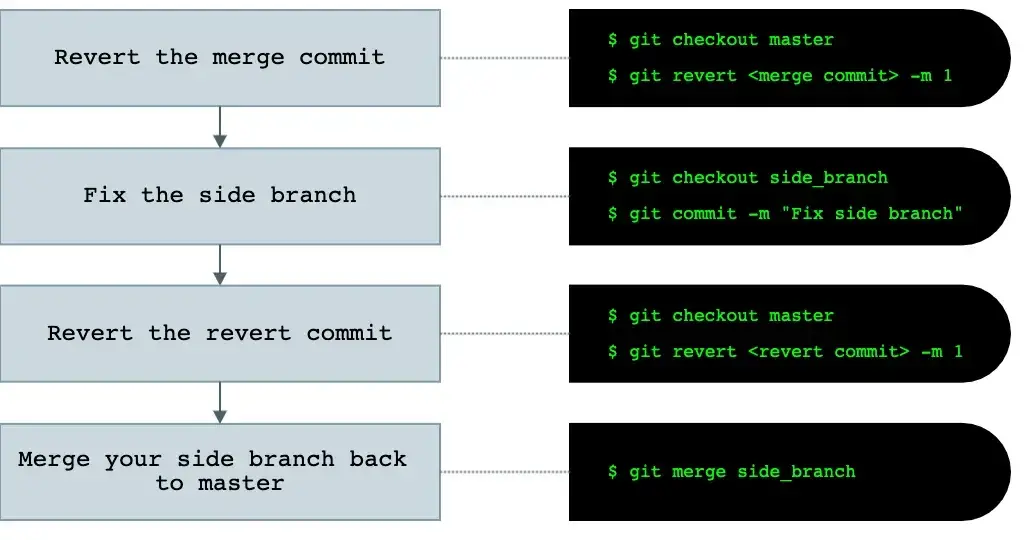
附上我自己的实验:
rm -rf .git A B C D E F && git init
echo 1 > A
git add -A && git commit -m 'init' # master: A="1\n"
git checkout -b topic
echo 1 > B
git add -A && git commit -m 'topic1' # topic: A="1\n", B="1\n"
git checkout master
echo 2 >> A
git add -A && git commit -m 'master1' # master: A="1\n2\n"
git merge topic --no-edit # master: A="1\n2\n", B="1\n"
git revert -m 1 HEAD --no-edit # master: A="1\n2\n"
git merge topic # Already up to date.
printf "1\n2\n" > B
git add -A && git commit -m 'after revert' # master: A="1\n2\n", B="1\n2\n"
git revert HEAD^ --no-edit # CONFLICT (add/add): Merge conflict in B ("1\n" v.s. "1\n2\n")
Fake merge
在 merge 的时候可以用 -Xours 或者 -Xtheirs 指定冲突文件的解决方案,这样使用的是递归策略:
$ git merge -Xours mundo
Auto-merging hello.rb
Merge made by the 'recursive' strategy.
hello.rb | 2 +-
test.sh | 2 ++
2 files changed, 3 insertions(+), 1 deletion(-)
create mode 100644 test.sh
也可以创建 fake merge,这样对于不冲突的文件也采用所选择的一方:
$ git merge -s ours mundo
Merge made by the 'ours' strategy.
$ git diff HEAD HEAD~
$
-s 选项是选择合并策略。
Subtree merging
原文给仓库添加了一个新的 remote 用来模拟 submodule 的行为,这个 remote 指向了完全不同的仓库(依赖)。然后将其文件放到本仓库的一个子文件夹中:
$ git read-tree --prefix=rack/ -u rack_branch
每次上游有更新时拉取最新代码:
$ git checkout rack_branch
$ git pull
合并也使用 -Xsubtree=rack 选项在子文件夹 rack 中合并:
$ git checkout master
$ git merge --squash -s recursive -Xsubtree=rack rack_branch
Squash commit -- not updating HEAD
Automatic merge went well; stopped before committing as requested
从形式上来看像将 rack_branch(实际上是不同的仓库)合并到当前 branch 中来。