chapter06 - linking
程序分段
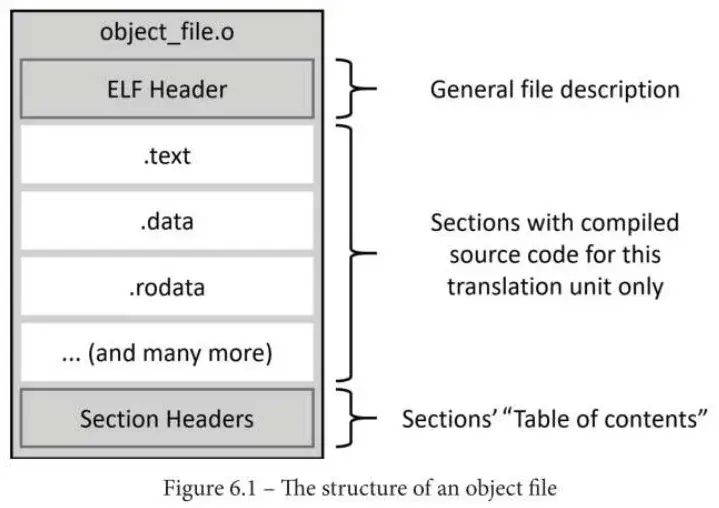
.text section: Machine code, with all the instructions to be executed by the processor
.data section: All values of the initialized global and static objects (variables)
.bss section: All values of the uninitialized global and static objects (variables), which will be initialized to zero on program start
.rodata section: All values of the constants (read-only data)
.strtab section: 常量字符串的表
.shstrtab section: 每个 section 的名称字符串的表
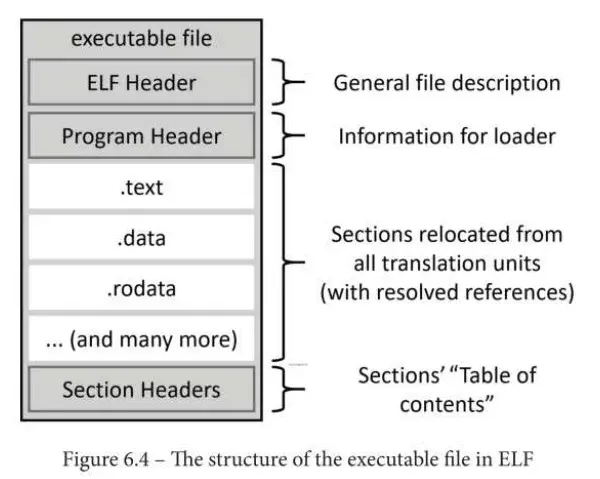
可执行文件有一些差异,其中之一就是 program header,它描述了创建进程镜像的信息。
库的分类
CMake 支持的有 STATIC, SHARED, MODULE:
MODULE
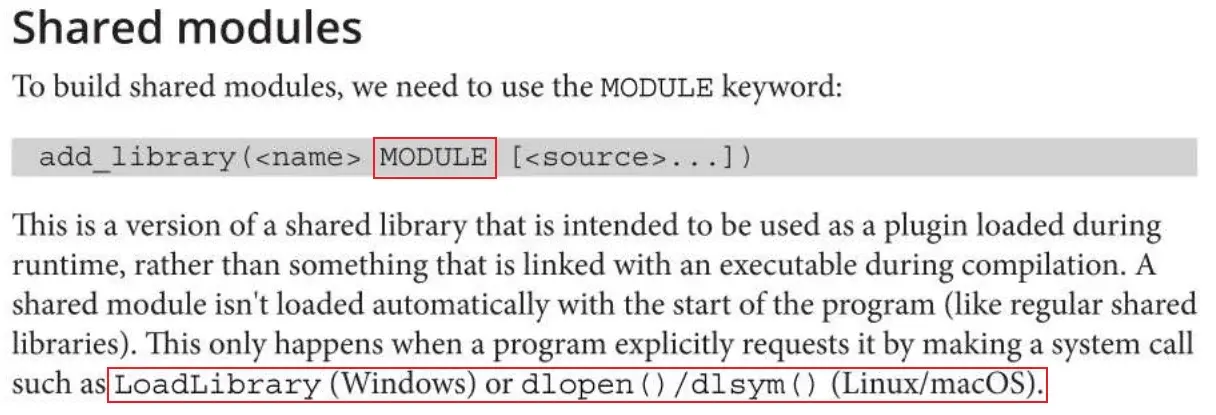
不应该将 MODULE 链接到其他文件。成为 MODULE 的库需要在运行时被显式链接。
Position-independent code
CMake checks the
POSITION_INDEPENDENT_CODEproperty of targets and appropriately adds compiler-specific compilation flags such as-fPICfor gcc or clang.
PIC will add a new section to our output - the Global Offset Table (GOT). Eventually, this section will become a segment containing runtime addresses for all the symbols needed by shared libraries.

感觉这里没有自动传播 POSITION_INDEPENDENT_CODE 是一个设计上的问题?不过 cmake 可以通过这个属性在传播目标上的一致性做冲突检查。
Dynamically linked duplicated symbols
动态链接时出现符号冲突,那么最终使用的符号和链接的顺序有关,而不是直接报错!
The order of linking and unresolved symbols
Linker 是比较笨的。只是简单按顺序从库中找到当前 unresolved 的符号,但是在处理库的时候可能会增加新的 unresolved 符号。如果在链接一个库时新增了 unresolved 符号,但是提供这个符号的库早就已经被 link 过了,而且后面也没有再次出现,那么就会出现问题。
这个时候要么更换顺序:
target_link_libraries(main outer nested)
要么 link 多次:
target_link_libraries(main nested outer nested)
还可以用特殊的 linker 选项:

Separating main() for testing


感觉不是很方便啊?