(CppCon 2018) 105 STL Algorithms in Less Than an Hour
- 为了简单,下面都不用
std名字空间了。而且实际上begin和end是有 ADL 的。 - 有一些算法是在
numeric头文件中的。
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2olsGf6JIkU
1 Not Classified (2)
1. transform
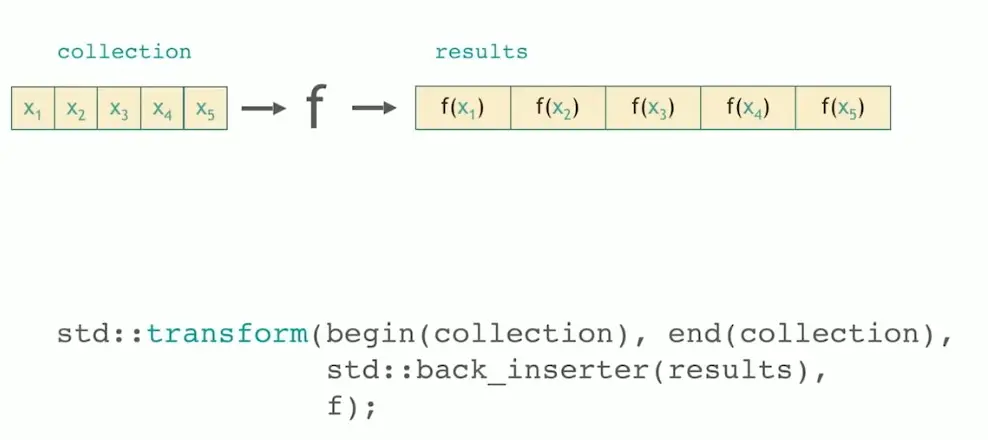
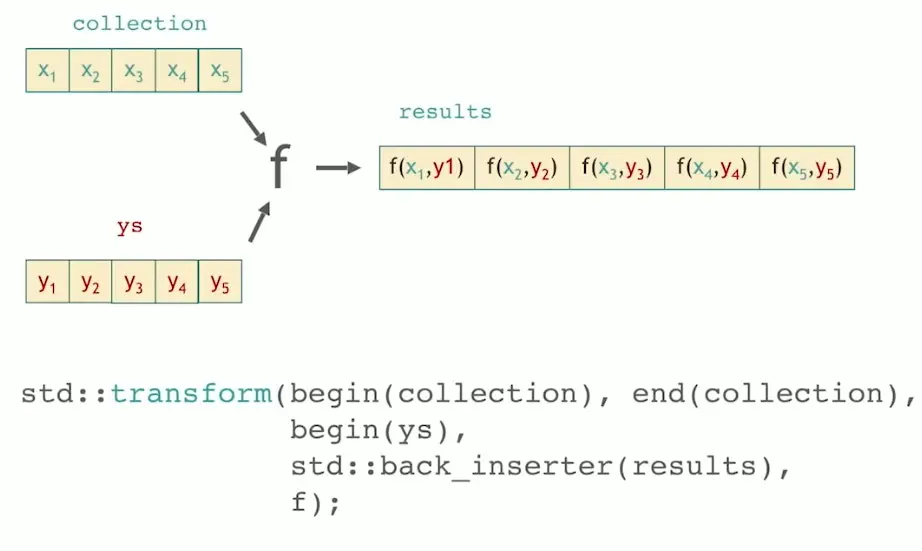
下面这种重载有点像先 zip 再 transform,但是没有 zip 灵活。
2. for_each 不关心选用的函数的返回值类型,主要配合有 side effects 的函数使用。
在现在有 for(*:*) 语法的情况下,for_each 也并不是完全没用。
1. 在需要按照一定顺序遍历,比如倒序遍历的时候,可以用 rbegin/rend/for_each 来完成。
2. for_each 可以指定执行策略,比如并行执行。
2 Permutations (17)
(逻辑)连续空间上的元素易位。
2.1 Heaps (4)
// 1: make_heap
make_heap(begin(v), end(v));
// 2. push_heap
v.push_back(4);
push_heap(begin(v), end(v));
// 3. pop_heap
pop_heap(begin(v), end(v));
v.pop_back();
// 4. sort_heap
// 相当于不停调用 pop_heap,但是每次不移除元素,而是将尾范围前进一个元素
sort_heap(begin(v), end(v));
2.2 Sorting (4)
// 1. sort
// 省略
// 2. partial_sort
// 找到 middle-first 个最小的元素放在前面,一般会用堆排序来实现
// 下面展示了函数重载之一
template< class RandomIt >
void partial_sort( RandomIt first, RandomIt middle, RandomIt last );
// 3. nth_element
template< class RandomIt >
void nth_element( RandomIt first, RandomIt nth, RandomIt last );
// 4. inplace_merge
// merge sort 的一部分
template< class BidirIt >
void inplace_merge( BidirIt first, BidirIt middle, BidirIt last );
2.3 Partitioning (4)
// 1. partition
template< class ForwardIt, class UnaryPredicate >
ForwardIt partition( ForwardIt first, ForwardIt last, UnaryPredicate p );
// 2. partition_point
// 找到分区完成的连续区域上的分区点!
// This algorithm is a more general form of `[std::lower_bound](https://devdocs.io/cpp/algorithm/lower_bound "cpp/algorithm/lower_bound")`, which can be expressed in terms of `std::partition_point` with the predicate `[&](auto const& e) { return e < value; });`.
template< class ForwardIt, class UnaryPredicate >
ForwardIt partition_point( ForwardIt first, ForwardIt last, UnaryPredicate p );
还有两个特殊的函数:
1. remove
2. unique

2.4 Other Permutations (5)
// 1. rotate
// 把左边区间的元素依次移走放到右边去。如果想要把右边的移走,可以用 rbegin 和 rend!
template< class ForwardIt >
ForwardIt rotate( ForwardIt first, ForwardIt middle, ForwardIt last );
// 2. shuffle
// 之前的 random_shuffle 被移除了,现在必须要提供一个随机数生成器才能使用
template< class RandomIt, class URBG >
void shuffle( RandomIt first, RandomIt last, URBG&& g );
// 代码片段:
std::vector<int> v {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10};
std::random_device rd;
std::mt19937 g(rd());
std::shuffle(v.begin(), v.end(), g);
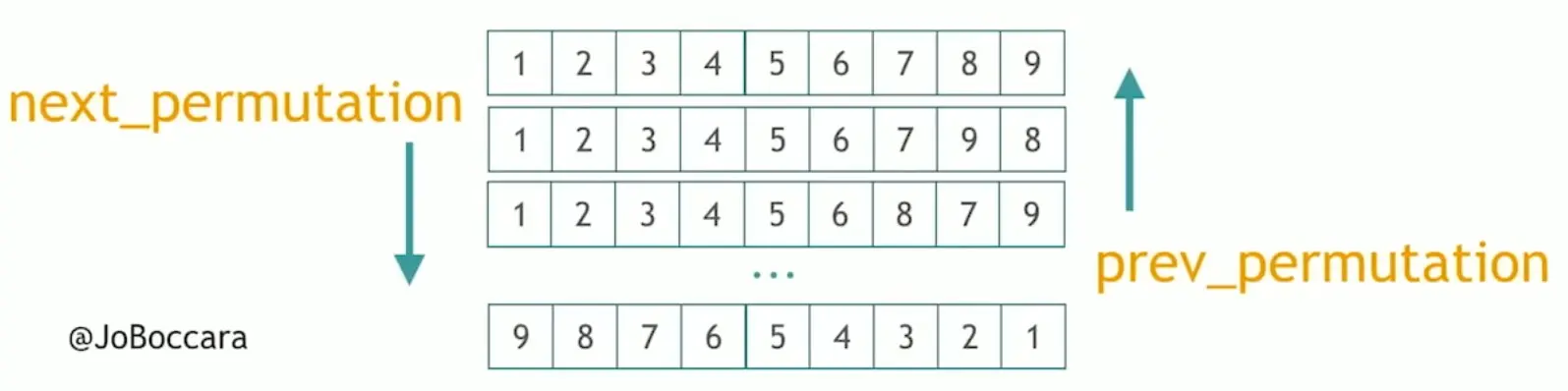
// 3. next_permutation
// 4. prev_permutation
// 这两个函数都是必须对存在一定顺序关系的序列进行易位的
// 5. reverse
3 Variants (34)
原视频说的是 Secret Runes,但是我觉得这里叫做变种会更加合适。
// 和上面 2.2-2.3 对应(因为堆没有稳定和不稳定的概念)
stable_* : stable_sort
: stable_partition
// 和上面 2.1-2.3 对应
is_* : is_sorted
: is_partitioned
: is_heap
// 和上面 2.1-2.3 对应
is_*_until : is_sorted_until
: is_partitioned_until
: is_heap_until
*_n : 11
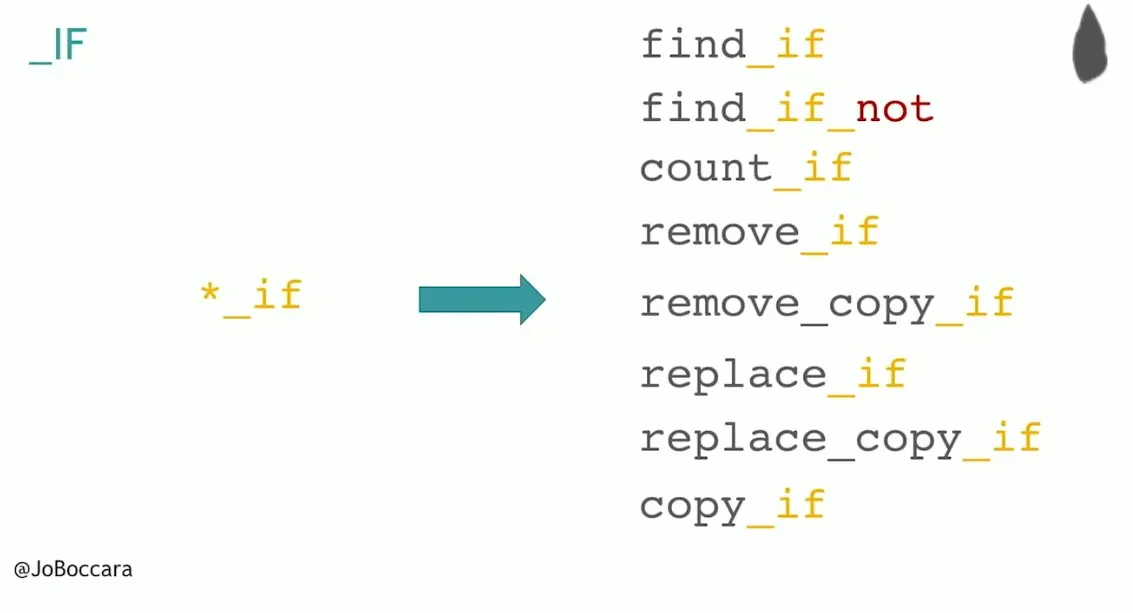
*_if : 8
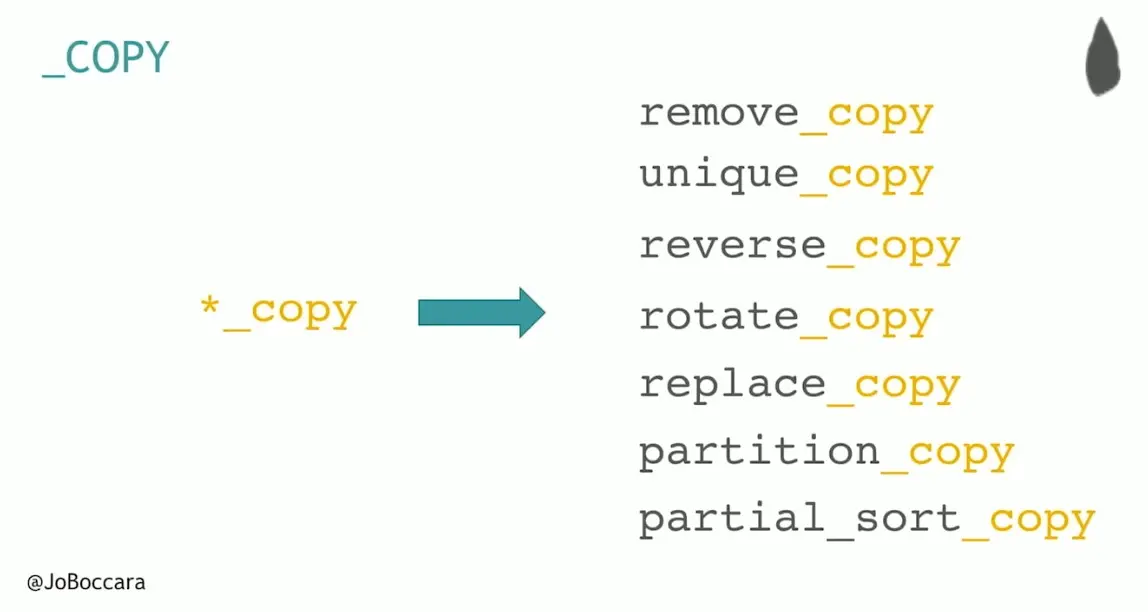
*_copy : 7

4 Numeric Algorithms (12)
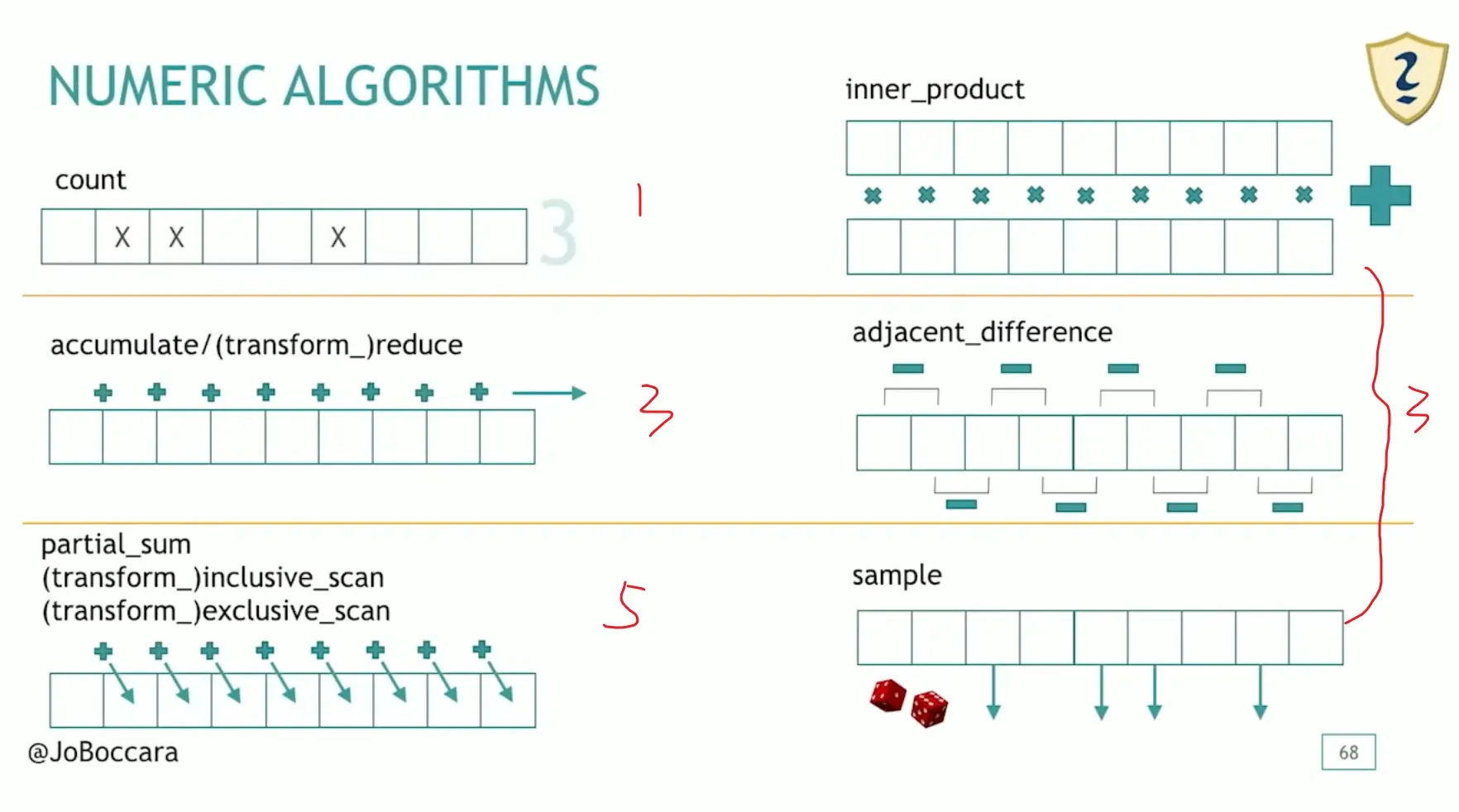
partial_sum 是用来计算前缀和的,相当于 inclusive_scan,只是功能没有那么多。带有 transform_ 前缀的函数都是先做元素转换,再参与规约计算(在 reduce 中是全规约,在 *_scan 中是两个元素做规约)的。
2024 年 1 月 21 日:accumulate 保证按顺序计算,reduce 不保证按顺序计算,所以必须有可结合性才能保证结果正确。
adjacent_difference:
template< class InputIt, class OutputIt >
OutputIt adjacent_difference( InputIt first, InputIt last, OutputIt d_first );
// If [first, last) is not empty, computes the differences between the second and the first of each adjacent pair of its elements and writes the differences to the range beginning at d_first + 1. An unmodified copy of *first is written to *d_first.
// 注意真正相减结果的位置是在 OutputIt 的下一个!当然相减运算符是可以重载的,可以改成加号(用来计算斐波那契数列)
std::array<int, 10> a {1};
std::adjacent_difference(std::begin(a), std::prev(std::end(a)),
std::next(std::begin(a)), std::plus<>{});
print("Fibonacci, a = ", a);
// Fibonacci, a = 1 1 2 3 5 8 13 21 34 55
sample:
// sample 是从序列中等概率不重复抽取 n 个(需要提供一个随机数发生器)
template< class PopulationIterator, class SampleIterator,
class Distance, class URBG >
SampleIterator sample( PopulationIterator first, PopulationIterator last,
SampleIterator out, Distance n,
URBG&& g );
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <random>
#include <vector>
int main() {
std::string s = "abcdefg";
std::mt19937 rng{std::random_device{}()};
for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++i) {
std::string out;
std::sample(begin(s), end(s), back_inserter(out), 4, rng);
std::cout << out << "\n";
}
}
/*
cdef
aceg
abfg
*/
这里用到了 back_inserter 就顺便提一下,标准库流对象是没有 back_inserter 的,它们用的是另外一个名称 ostream_iterator,使用的时候需要模板类型参数:
#include <iostream>
#include <iterator>
#include <numeric>
#include <sstream>
int main()
{
std::istringstream str("0.11 0.22 0.33 0.44");
std::partial_sum(std::istream_iterator<double>(str),
std::istream_iterator<double>(),
std::ostream_iterator<double>(std::cout, ", "));
std::cout << '\n';
}
// 0.11, 0.33, 0.66, 1.1,
5 Query a property of Sequence(s) (7)
对一个序列查询:
all_ofany_ofnone_of
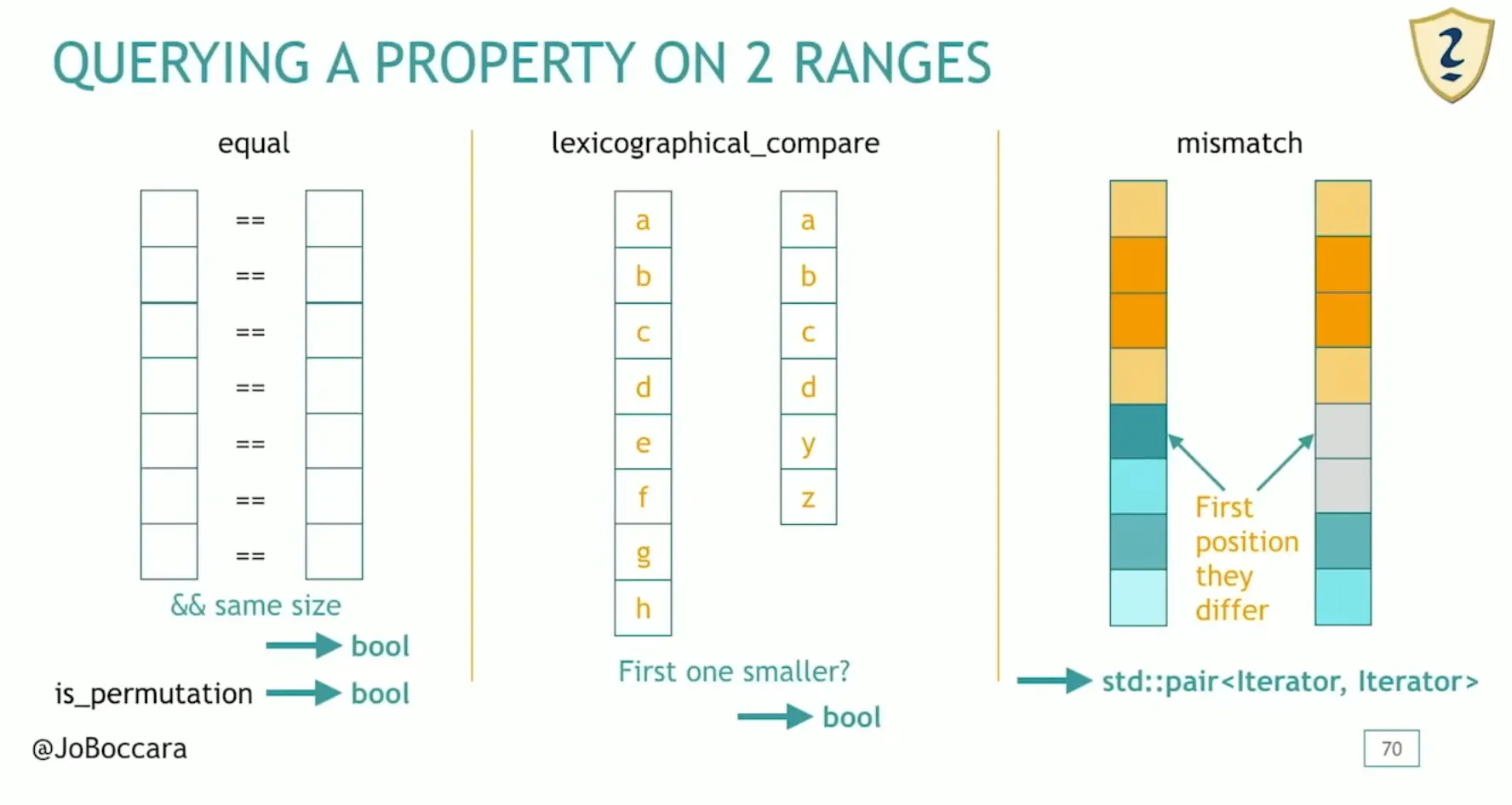
对两个序列查询:
equal:判断两个序列是否相等(借助反向迭代器可以判断序列是否回文)is_permutation:判断第二个序列是否是第一个序列的一种排列lexicographical_compare:可以按照字典序做小于比较的判断(还有一个 three_way 的版本)mismatch用来找到两个序列中第一对不能匹配的迭代器
6 Search a Value/Range (12)
Not sorted:
find:这个是 O(n) 复杂度!并不是在已经排序的序列上二分查找adjacent_find:找到序列中第一次出现两个相等元素的位置(可以传入函数对象使得相等比较被改写)
Sorted:
equal_rangelower_boundupper_boundbinary_search:只返回在还是不在,不返回具体的位置!
Searching a range:
search:就像在字符串里面找子串一样。除了一般的两对迭代器的查找方式外,还能传入一个 searcher,比如非常出名的boyer_moore_searcher,std 中有其实现。find_end:仍然是在子序列,但是从末尾开始。可能改名为search_end比较合适。find_first_of:在第一个序列中查找第二个序列中出现的任何元素的第一次出现位置。
Searching a relative value:
max_elementmin_elementminmax_element
7 Sets (6)
感觉像数据库中的集合概念。不是真正的无重复集合,有点诡异。
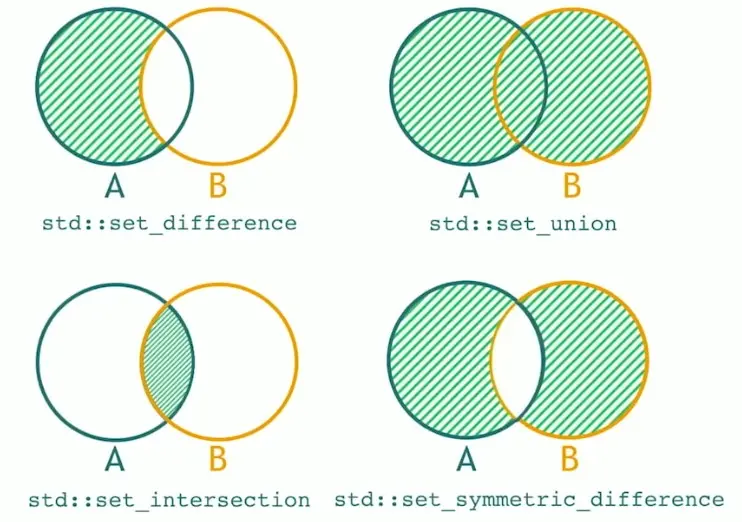
set_difference: 在第一个序列但不在第二个序列的元素(相当于 - 号吧),要求两个序列是有序的!set_intersectionset_union:向 OutputIter 中输出在两个序列之一的元素,会按单个元素去重!而merge是完全不会去重的。set_symmetric_differenceincludes:检查序列 A 是否包含序列 Bmerge:归并。是inplace_merge的非 inplace 版本。
set_difference 只会删最多一个元素,下面的 3 个 5 没有删完
{ 1 2 5 5 5 9 } ∖ { 2 5 7 } = { 1 5 5 9 }
set_intersection
{ 1 2 2 3 4 5 6 } ∩ { 2 2 3 3 5 7 } = { 2 2 3 5 }
set_union 去重了,但是又没完全去重
{ 1 2 3 4 5 5 5 } ∪ { 3 4 5 6 7 } =
{ 1 2 3 4 5 5 5 6 7 }
8 Copy (5)
1. std::copy(first, last, out)
2. std:move(first, last, out)
3. std:swap_ranges(first, last, out) 能够交换等长序列
4. std::copy_backward 能够解决那些顺序相关的问题(尤其是在两段序列有重合部分的时候)
5. std::move_backward
9 Value Modifiers (4)
1. fill(first, last, x)
2. generate(first, last, func)
3. iota(first, last, init)
4. replace(first, last, old_v, new_v)
11 Raw Memory (6)
fill/copy/move 都用了 operator=,但是都要求赋值运算符左边的对象必须首先被构建(当然,对 POD 直接赋值是没有问题的)
1. uninitialized_fill
2. uninitialized_copy
3. uninitialized_move 用的是移动构造函数(如果有)
4. uninitialized_default_construct
5. uninitialized_value_construct
6. destroy(first, last) 是对一个系列上的对象调用析构函数